Acute prostatitis is an acute inflammation of the prostate gland caused by an infection.With this disease, swelling of the prostate forms, and purulent foci appear in its tissues.Statistical data gives us the right to assert that acute prostatitis in men is a common disease;With age, the risk of its occurrence increases.
The effectiveness of acute prostatitis treatment directly depends on the timeliness of the patient's treatment.This disease quickly develops into a chronic form, the treatment of which is longer and more complex.
Acute form of prostatitis
If we talk about the clinical development of acute prostatitis in men, there are three forms (stages) of the disease:
- catarrhal;
- Follicular;
- parenchymatous.
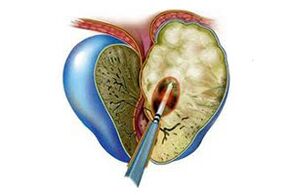
The first to occur is catarrhal inflammation, which is characterized by melting of acini and the appearance of reactive edema of interstitial tissue.This leads to a significant enlargement of the prostate gland.The next stage is the rapid spread of the inflammatory process to the lobules and excretory ducts of the prostate.We are talking, in particular, about the excretory duct of the prostatic gland that leads to the posterior part of the urethra.Inflammatory changes affect only the mucous membrane.Excretory ducts lose their contraction, they narrow significantly or become completely blocked, creating an obstacle for the release of prostate secretions.The catarrhal form is directly related to infectious pathogens that have migrated from the posterior part of the urethra.Since the inflammatory process also affects the secretion of the prostate, it can trigger the appearance of posterior urethritis.
During the follicular stage, the focus of inflammation reaches and spreads throughout individual lobules or the entire prostate gland.Purulent foci appear, pus enters the urethra.Prostate enlargement does not stop;Tissues undergo destructive changes.
During the parenchymal phase of acute prostatitis, the inflammatory process affects the interstitial tissue of the prostate gland.This stage occurs after the penetration of infectious pathogens through contact or the hematogenous route, for example, after surgery.
Parenchymal prostatitis at the beginning of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of single pustules, which during the development process unite and combine with prostate abscess.
As for follicular and parenchymal forms, during their development, inflammatory changes often occur in the posterior part of the urethra and bladder neck.
Prognosis and prevention of acute prostatitis
In the majority of cases, etiotropic therapy, performed on time, can eradicate the signs of acute prostatitis.If treatment is not carried out, it is quite possible for an abscess to occur or for the disease to become chronic.
Prevention of this disease usually means timely treatment of infectious diseases in the body, as well as identification and treatment of venereal diseases and urethritis.A man needs to lead a healthy lifestyle, especially paying attention to increased physical activity.Also, the development of this disease is prevented by a regular sex life and the absence of unprotected casual intercourse.Strict adherence to the rules of personal hygiene is another important requirement for a man at any age.
Cause of disease
Acute prostatitis in men can occur at any age.The reason is often the penetration of various infectious pathogens.This is E. coli, but there are also Streptococci, Staphylococci, Candida Fungi, Chlamydia, Trichomonas.The most common route of entry is the excretion tract.Pathogens can also enter the prostate gland from the bladder, which is undergoing an inflammatory process (for example, acute cystitis).The infection can also spread from a purulent focus located in the immediate area.
The inflammatory process in the prostate caused by the presence of microorganisms can occur for various reasons.Factors that increase your risk include:
- surgical intervention in the area of the urethra;
- unprotected sexual intercourse, inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract in partners;
- use of urethral catheters;
- prostate stones, etc.
The occurrence of acute prostatitis may not be associated with infection.It can occur as a result of a sedentary lifestyle, hypothermia, and various disorders that lead to stagnation in the pelvic area.
Symptoms of acute prostatitis
Since there are various stages of acute prostatitis, the symptoms of the disease often depend on them.But there are general characteristics that unite all forms.First of all, it is pain, general hangover, as well as problems with the urination process.
The catarrhal form is usually accompanied by severe pain, heavy feeling in the perineal area, frequent urination, accompanied by painful sensations.During palpation, the doctor may notice an increase in the size of the prostate gland.Secretion test results may show high levels of white blood cells.
Symptoms of acute prostatitis in follicular form are more obvious.A man feels pain in the perineum, radiating to the sacrum or penis.The process of urination is accompanied by pain, urine is retained, and difficulty with urination often occurs.There is general weakness and the patient has a fever.Palpation shows an enlarged prostate, its outline becomes asymmetric.Focal pain may occur.Tests show an increase in the level of leukocytes and the presence of purulent threads in the urine.
The parenchymal form is accompanied by a significant increase in body temperature, the value can reach 39.5 degrees.Common symptoms are pronounced: shivering, loss of appetite, and lack of strength.Urination is delayed, the process is accompanied by severe pain.Passing water is also difficult, and constipation becomes severe.
In such cases, it is necessary to immediately start treatment for acute prostatitis.If the process is initiated, there is a high probability of prostate abscess, paraprostatitis, phlebitis of the paraprostatic venous plexus.If the patient does not see a doctor, the disease becomes chronic, and the possibility of complete recovery is significantly reduced.
Diagnosis of acute prostatitis
When the patient contacts the urologist, the doctor diagnoses acute prostatitis, identifying the stage of the disease.Experts receive information after conducting a comprehensive study.The methods used in the diagnosis in this case consist of physical, instrumental, and laboratory studies.
Physical examination consists of examining the state of the prostate gland from the rectum.Thus, the specialist gets the opportunity to assess the size, shape, consistency of the organ, and the presence of pain.As a result of the analysis of the secreted secretion, it is easy to determine a decrease in the amount of lecithin grains and an increase in the level of leukocytes.
Palpation of the gland also involves the collection and transfer of urine for examination.In most cases, acute prostatitis is marked by an increased level of leukocytes.Urine culture, PCR and blood culture, and urethral discharge analysis are also prescribed.
The instrumental method in the case of this disease is represented by ultrasound diagnostics performed transrectally.If the patient has severe pain, the choice of examination is the transabdominal method.
When the question of surgical intervention arises, it becomes necessary to carry out CT and MRI of the pelvis.
Treatment of acute prostatitis
Treatment of acute prostatitis is carried out in a hospital setting.This is due to two factors.First, there is the risk of serious complications that can affect men's health and further affect reproductive function and erection quality.Second, the disease is complicated, accompanied by obvious symptoms and painful sensations.Treatment of acute prostatitis begins with drug therapy, prescribing etiotropic drugs to the patient.The most important role is played by antibacterial agents that suppress the function of microorganisms.
To reduce the severity of pain, as well as to relieve spasms, patients are recommended to take antispasmodics and analgesics.Sometimes heat enemas and rectal suppositories are used to alleviate the condition.After overcoming the acute symptoms, it becomes possible to use physiotherapy.This procedure improves microcirculation, improves local immunity, and helps eliminate inflammation.Among physiotherapy methods to treat acute prostatitis, the most effective is prostate massage, as well as microwave therapy and electrophoresis.For many years, prostate massage has been considered a very popular measure, which helps eliminate congestion;It is also recommended to be used regularly as a preventive measure for men who have reached the age of forty.
If there is a problem with the urinary process, the catheter is not used;Instead, Trocar cystostomy is preferred.
Recovery is considered the regeneration of prostate tissue, the restoration of its function, while laboratory tests show that infectious pathogens are not present, and prostate secretions return to their normal composition.
Surgery is not a widely used treatment for prostatitis.It does not always bring results.Surgical solutions bring positive dynamics in less than half of cases.The most common side effect of the operation is erectile dysfunction, retrograde ejaculation is also common, where during ejaculation sperm enters the bladder, and sometimes narrowing of the ureter occurs.Surgical methods do not guarantee recurrence.Therefore, surgical intervention is only used in certain cases, such as:
- occurrence of prostate abscess, which must be opened and cleaned;
- lack of results from treatment using conservative methods in the form of drugs, traditional medicine, physiotherapy procedures;
- development of serious complications;
- the presence of an inflammatory focus in the pelvic area;
- formation of paraproctitis (purulent abscess in the cells localized around the rectum);
- the presence of blood in the urine;
- urinary retention and cessation of urination (anuria);
- the presence of stones in the bladder, kidneys, the cause of which is prostatitis;
- suspicion of malignant tumor.